Previous post
Sistrix in detail, the online visibility index that has been standardized
We understand as onpage SEO to be the set of actions that we carry out to optimize the website in view of its behavior in search engines, and whose ultimate goal is to achieve positions in the SERPs that result in increased organic traffic, which comes directly from search engines.
There is a long list of On-Page interventions that can be carried out on a website with the aim of improving it. Below, we explain some of the most important ones.

URLs Friendly
URLs where the main keyword appears between the first 3-5 words have more weight in the natural positioning. This means that we must avoid meaningless URLs (with strange numbers or parameters), betting on natural addresses, with the keyword expressed clearly.
mydomain.com/frequently-asked-questions
Short URLs
Don’t try to dump all the web content into the URL: studies have shown that the best wording when indexing and ranking is short and with the keywords being attacked separated by hyphens.
mydomain.com/how-to-index-urls
- Use dashes (-) to separate the words that will form the URL
- Do not use underscores in the URL or other strange characters
Keyword in the title
You know that each URL must attack a unique keyword with a specific search intention, so it is best to make it clear as soon as possible what that keyword is: use it in the title of the page, better the more at the beginning, so that Google has no doubts about what it is.

Optimize image alt
Similarly, do not miss the opportunity to enter your keyword in the images that accompany the content of the URLs, since in addition to promoting positioning, you will contribute to improving the accessibility of the web (the alt attribute replaces the image if, for some reason, it is not displayed).
Use a variant of the keyword in the H1
The H1 corresponds, usually, to the headline of the URL, the first header that we see when we access it and that “summarizes” the information it contains. Use this tag to explain to your users and the search engine what they can find in the URL.
Avoid the cannibalization of keywords
We understand by cannibalization the fact that Google hesitates between two or more pages of the same website when positioning them for a specific keyword, so that both compete with each other in the ranking, which in the end prevents the ranking of both.
We must make sure that each of the URLs on our website are oriented to a single keyword with a defined search intention. If we detect that there is more than one URL for a specific keyword, we must opt to unify both contents and redirect the weaker one to the stronger one, or to establish a strategy for creating semantic content that differentiates both definitively, depending on their importance to the overall strategy.
Write the metadescription to increase traffic
Although the metadescription itself does not contribute to the positioning of the website, the insertion of Rich Snippets (as explained above) and a correct wording, using the semantic field of the keyword we are working on, with a call to action, can contribute to increase the organic traffic of the page.
Insert the keyword as soon as possible in the text
As we have already mentioned, you should not create doubts for Google about which keyword you are working on in each specific URL. It is highly recommended that, in addition to the H1, it appears in the first paragraph of the content, as well as several times throughout (be careful, without making Spam, potentially punishable). It uses variations of it, synonyms and all its semantic field to avoid annoying Google.
Don’t neglect internal linking
Developing a link strategy from each related URL within your website has a double benefit: on the one hand, you make it easy for the Google spider to access all the URLs on your website, while on the other hand, you provide information to the user, improving their browsing experience.
Do not abuse the exact keywords in the link
As in the writing of the content, use variations of the main keyword and longtails when inserting links to other URLs on your website, looking for ease in them. The opposite is considered keyword stuffing and is potentially penalized.
Use original images and video to enrich the content
You will bring added value to the user, you will get original and unique content for your page and you will bring a different point of view from the rest of the webs of the same subject.
Write a visual content
The content of your website must not only be of quality and original: it must be laid out in such a way that it is visually attractive to the user. Avoid long paragraphs, insert bold type in the main ideas, so that the reader can find them at a glance, and use listings and enumerations to visually lighten the texts.
Optimizes the crawl budget
The crawl budget is the time credit Google gives your site to be crawled by the bot: larger and more authoritative sites have a higher crawl budget.
Make it easy for the search engine: the implementation of breadcrumbs and correct internal linking makes it easier for spiders to know where to go and be able to crawl the whole site more efficiently.
Cleans and optimizes the HTML
It is up to the layout designer to implement a simple template in HTML, with the least amount of code possible and written in a clean and simple way, which will result in fewer elements loaded into the DOM and, therefore, a shorter loading time for the website.
Refer your users to related content
If you make it easier for the user to find the content related to the URL they are viewing (similar products, related information, etc) you make it easier for them to visit more pages within the site, increasing the time they stay on the site.
Works to improve the UX (user experience)
All the design of the web from being oriented to improve the user experience, which is for whom we are working, after all.
- It presents the structure in a simple way, so that the user finds what he is looking for at first glance.
- Make a modern and attractive design, avoid outdated templates
- It is essential that the content looks just as good on any type of device, whether it is a desktop, laptop, tablet or smartphone. Google Search Console features a tool that will tell you how your website is doing in this respect.
- It avoids the loading of interstitial, pop ups and javascript, which can affect the positioning of the website.
- It works to reduce the loading time as much as possible, especially in mobile. 3 seconds is an eternity for the person who consults a website from his mobile, most likely in that time, has gone, greatly affecting the bounce rate of your website.
Check that you have correctly implemented the web hreflang
If you are going to follow an international strategy, it is fundamental that you implement this label in the header to indicate the different languages in which you are going to work with on the web.
Use the favicon
Although there is some controversy about whether or not it directly affects the SEO of the web, our recommendation is that you include it in the header of the page: in the worst case, if we assume that it does not affect the SEO, it will contribute to the identification and association of your brand with the web.
Encourages user feedback
In addition to establishing a direct communication channel with your users, you favor generating original content “automatically” and without allocating your own resources to it.
Sitemap XML
Establishing a web map is one of the best ways to facilitate the tracking of the web by search engines. When creating it, make sure
- Only include the URLs you want to position
- It does not include any URL with a status code other than 200 (if not, take the opportunity to correct them).

Sitemap HTML
The HTML sitemap has a double benefit, since it not only benefits the search engine bots, but also the web users themselves, who can easily find the contents they are looking for within the web.
Tag rel=next/prev
These HTML tags were used to reduce duplicate content and we could interpret it as a possible crawlability improvement in the interrelations between web pages, helping Google as an indexing signal applicable to the optimization of listings. Well, since in March 2019 we found out that Google had not been using it for a few years… and had not informed anyone about it.
Publish the best possible content for the keyword you want to rank
Although there is no direct correlation between the quantity of content and its quality, it is true that it is very difficult to compete in the sea of the Internet with a text of 400 words, especially if it is a concept with a lot of competition.
Try to write the best possible original content for each concept without setting limits on length.
- Use synonyms, related terms and semantic fields to enrich your texts. In this way, you will be better positioned against the competition, Google will take you as an expert on the subject which you write about and you will keep at bay the danger of keyword stuffing.
- Design a logical header structure. Use the H1-H5 tags to order and show the concepts you are going to talk about in a logical and descending order of importance, so that a table of contents is created that can also guide the user about what to expect from the page.
- Create unique content. We won’t get tired of repeating this: unique and original content is the king. Use your knowledge about your product or your niche to provide original content that no one else has, giving your website added value.
Prioritizes the loading of HTML and content
This way, you get that when the crawler crawls the web it finds the information as soon as possible, which will benefit your crawl budget and will result in a better positioning.
Beware of “above the fold” content
The above the fold content is the one that the user sees instantly when entering the website, without the need to scroll. Try to have all the important information on your website appear at first glance.
Design a simple web architecture
To make things easier for both the search engine and the user, always try to avoid having URLs that are more than three levels deep, that is, that require more than 3 actions from the home page. If you have many URLs below that level, you should consider a redesign of your architecture.
Mobile SEO Optimization
Currently, there are 3 ways to adapt a website to the requirements of mobile device browsers.
Responsive Web Desing
Responsive design consists of a CSS3 code that manages to display the same content regardless of the type and size of the screen by using a grid and a flexible design, which adapts automatically.
Dynamic serving
In this case, the content is provided with different HTML and CSS depending on the user agent making the request, i.e. depending on whether or not the request is made from a mobile, tablet or desktop.
It is necessary to adapt the functionality with each new model of smartphone or tablet that comes onto the market, as until it is adapted to this it does not work, showing the content as it would on a desktop.
Separate domain or sub-domain
In this case, the desktop and mobile contents will be hosted in different URLs, which means that the user experience will also be different.
It means providing content for mobile and desktop users at different URL’s, usually using for the mobile version a URL with .m or through a subdomain of the main URL. This implies that the user experience will be different as well.
If we decide to implement this option, we must take into account:
- We must redirect users to the corresponding page depending on the device from which they access the website.
- Execute the redirection only if we are sure that we have a page that is correctly displayed on mobile devices.
- Check that the loading of the website is done in a reasonable time, to avoid interfering with the user experience
- Reduce redirections as much as possible
- Avoid the load of interstitial advertising, which slows down the load of the web and therefore affects the positioning in search engines.
WPO or Performance Audit
The WPO refers to the loading time of our website compared to competitor websites. Our goal should be to reduce as much as possible that loading time, both in Desktop, and especially, in mobile.

To do this, it is necessary to consult all the technical improvements available and implement as many as possible, taking into account that each website has special features in terms of technical or security restrictions, for example, which prevent us from implementing all the improvements we would like.
However, there are very simple interventions that are within the reach of anyone that can considerably reduce the loading time of our website.
Reducing the size and weight of images
Uploading an image to the web at a size larger than what you are going to see will increase the loading time of the image in a useless way. Optimizing them to reduce their weight and publishing them in the size in which they are going to be displayed helps to reduce loading times and, therefore, the user experience.
Avoiding massive redirections
Reducing the number of redirects, either temporary (302) or permanent (301) prevents the crawl from wasting resources by moving from one page to another.
Prioritize the loading of the content you want to position
You can modify the order of loading the files in the DOM using javascript, so that the spiders initially find the HTML content and then those files that do not contribute to the positioning of the web in SERPs.
Remove unused CSS
Removing all unused files from the website helps to speed up the upload by avoiding the download of useless information. This is especially important when it comes to unused style sheets.
Use a CSS preprocessor
This type of program optimizes the code, which makes the style sheets smaller and lighter, which favors the loading time.
Reduce the number of errors 404
The less time the crawler spends crawling pages that don’t provide information, the more time it will take to crawl the rest of the correct URLs and favor their indexing and positioning.
Minimize the elements that load in DOM
Similarly, reducing the number of elements that load first on the web favors the speed of that first load.
Reduce the favicon
Although there is still some controversy about whether or not the favicon affects SEO positioning, it is certainly an element that favors brand branding. It is recommended to use a favicon that is as small as possible and allows for caching.
Delete unnecessary plugins
There are tools that can help you to detect the plugins installed in your WordPress that you do not use or that you are not getting the most out of.
Minimize the code
When you miniaturize the code (HTML, JS and CSS), you reduce the number of lines the bot has to process, which speeds up the rest of the processes. There are specific plugins to minify the code in each CMS.
Adapt the server to the HTTP2 standard instead of HTTP
The HTTP/2 protocol is an enhancement of the classic HTTP that works over TCP/IP optimizing the performance in the client-server communications, improving the rendering time and reducing the load.
Force Trailing slash
As we have already mentioned on other occasions, the fact that at the end of the URL a bar appears or not actually generates different URLs that, in addition, cause content cannibalization, as they show the same content. To avoid this, a redirection can be made from one to the other or, better in terms of search engine optimization of the web, implement it in the .htaccess file.
Tools for SEO Audits
Google Search Console
It is a free tool provided by Google, which allows you to analyze the state of the web based on its organic traffic results, offering data from SERPs, links, indexing status, crawl or server errors… To use it you only need a Gmail account.

Google Analytics
Like the previous one, it comes from the Google universe and its free to use, although in this case it is oriented to the analysis of web traffic, organized by traffic sources, type of acquisition, user behavior and conversions, among others.
It is a very complete tool, which allows downloading personalized reports, as well as creating segments to filter the available information and analyze the result of marketing campaigns with data from sessions, bounce rates, average session duration, most viewed content, achievement of objectives…

Screaming Frog
This is, without a doubt, the most famous crawl and an essential tool for technical audits: the frog’s program behaves just like the Google bot would, showing after analysis very important information, such as titles and metadescriptions, URL headers structure, low quality content and duplicates, response codes of the different URLs… Each one of Screaming Frog’s reports allows you to attack an aspect of the web for its best optimization.

Chrome Extensions for Technical SEO Audits
In addition to the above programs, Google offers several extensions with which we can complement the data collected for a technical audit.
Moz Bar
It shows us the meta tags ( URL, Title Tag, H1 and Metadescription ) of the contributed URL, at the same time it analyzes the links found in the content and classifies them into follow, no follow, external and internal. In addition, it shows us the values of the Page Authority (PA) and the Domain Authority (DA).

Web Developer Toolbar
It allows checking of the status of technical SEO aspects, such as alt attributes on images, links or headings (H1, H2, H3…) of the page. In addition, with this extension we can disable CSS to check if the bot displays the same version as users in their browsers.
PageSpeed Tools
It is also important to have appropriate tools to check the loading speed of the web and in what order the elements are loaded into the DOM.
GTMetrix
The tool shows us the time it takes to load the first byte, as well as the loading time of the rest of the elements, shown in a graph in the form of a cascade.
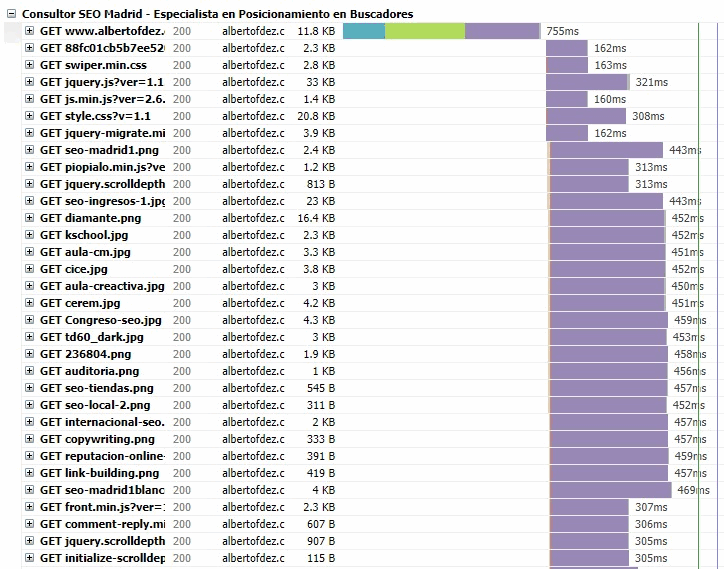
Pingdom Tools
Identifies bottlenecks in web performance by showing the loading times of each of its parts and ordering the results.

Webpagetest
This free web tool performs various tests, using real browsers (Internet Explorer and Google Chrome) from different countries around the world, for which it sets up tests of varying complexity.
The results include image and video loading simulations and suggestions for improvement, among others.

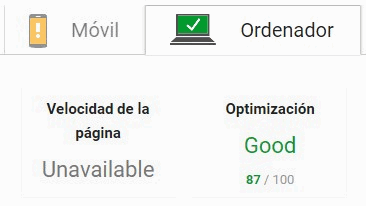
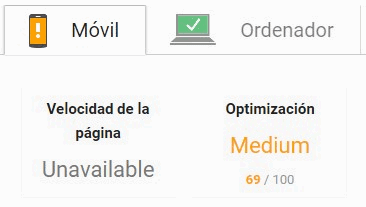
PageSpeed Insights
This tool measures the level of optimization of a website on desktop and mobile, simulating the user agent of each one and giving a score from 0 to 100 points: the better the score, the better the website will be optimized.